In the field of power electronics, such as frequency converters, new energy vehicle electronic control systems, and industrial high-power power equipment, isolated gate drivers are an important part, especially in the application of MOSFET or IGBT, which can provide safe and efficient gate control. Gate drive optocouplers are key components that integrate photoelectric isolation and power amplification functions, mainly used to connect and isolate low-voltage control circuits with high-voltage power circuits. Such optocouplers are suitable for driving power IGBT and MOSFET, and the higher output voltage can meet the gate voltage drive requirements of power devices. Its core features and advantages are as follows:
- High isolation voltage:It is possible to achieve an isolation voltage of more than 2500Vrms, meeting the safety specifications of high-voltage systems;
- Strong anti-interference ability: Optical transmission method is not affected by external electromagnetic fields (EMI), ensuring the integrity of signal transmission in a noisy environment;
- Packaging diversity:The packaging format and pinout should adapt to different application requirements, such as board-level space constraints, thermal requirements, and interconnect with other components;
- High reliability:The design without mechanical contacts makes it have a longer service life, and it can work stably in a wide temperature range of - 40℃~125℃, suitable for harsh environments such as industry.
Internal structure and working principle
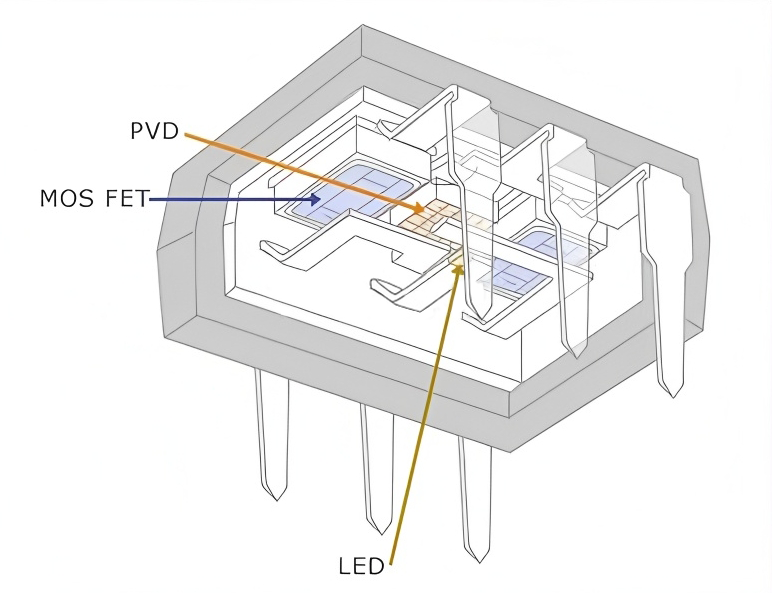
Schematic diagram of the internal structure of the gate drive optocoupler
The gate drive optocoupler consists of a light emitting diode (LED) and a photodetector that integrates the drive circuit (usually a photodiode + amplifier circuit).
Its working process is actually very simple, just like a set of "signal relay + amplification":
- Firstly, the low-voltage control signal drives the input side light emitting diode (LED) to convert the electrical signal into an optical signal;
- The optical signal is transmitted to the receiving end through an insulating medium and is received by the photoelectric device and converted into a corresponding push-pull pulse low-power signal;
- Finally, the current signal is power-amplified by the internal integrated high-speed drive circuit, forming a push-pull pulse high-power signal, and the output voltage and current meet the requirements of the IGBT gate, directly controlling the turn-on and turn-off of the IGBT.
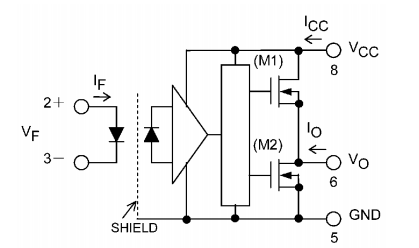
Gate drive optocoupler working principle flow chart
Core functions and application scenarios
Gate drive optocouplers are key components in servo motor drives and industrial frequency converters, and their internal integrated core functions can be decomposed into two parts:
- Electrical isolation between the input and output sides is achieved through optical signal transmission, preventing the influence of high voltage and current on the control circuit;
- Amplify the weak control signal so that it has sufficient voltage and current to drive the IGBT, which can quickly charge and discharge the capacitor of the IGBT gate, ensuring that the IGBT can stably conduct and cut off.
Typical application scenarios
- Servo motor
The optocoupler is responsible for transmitting the drive signal to power devices such as IGBT/SiC MOSFET; fast signal transmission ensures high-precision speed and positioning control of the motor, isolating electromagnetic interference, protecting the chip, and reducing motor vibration and positioning deviation.
- Industrial Inverter
The optocoupler is responsible for transmitting the PWM signal, controlling the conduction and switching of the IGBT and other switching tubes, to achieve voltage and frequency regulation; at the same time, it isolates the low-voltage control side from the high-voltage power side, prevents high-voltage crosstalk, and ensures safety; and can adapt to the harsh working conditions of industrial high and low temperatures and strong interference environment.


